Lab 8: Kotlin Object Orientated Programming
Welcome to the Kotlin Banking System workshop/lab! In this session, you will learn how to create a simple banking system using Kotlin. The system includes classes for BankCustomer, FundsController, ATM, Hashing, and ErrorMessage.
Step 1
-
Open IntelliJ
-
Create a new project
- Call it
BankingSystemlike the screen shot below. - Tick 'Add sample code'
- Note you can use any JDK for this exercise, I am using JDK 17.0.6.
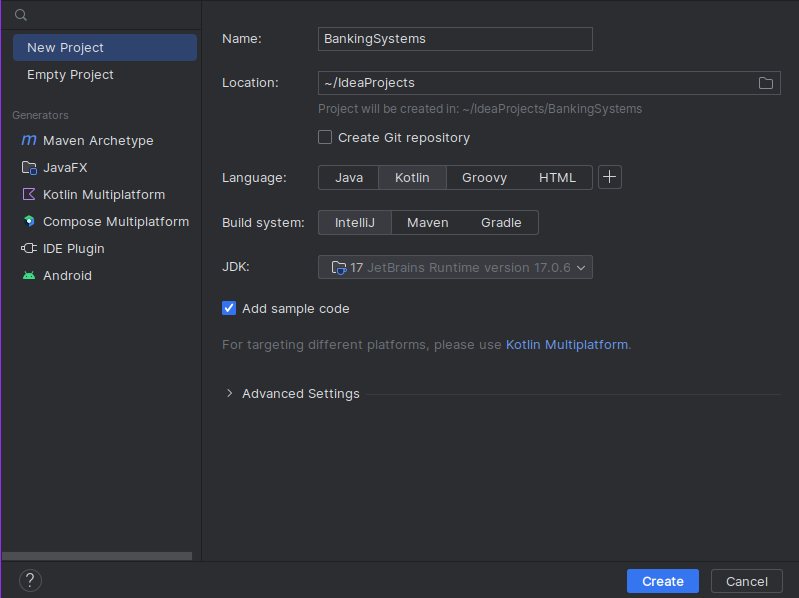
- Call it
Step 2
Create five Kotlin class files:
ATMBankCustomerErrorMessageFundsControllerHashing

Step 3 - ErrorMessage Class
Open the ErrorMessage.kt file and let's make our own error message function that can be called across other classes.
- The function below, will take in a message we supply and use the
Exceptionclass tothrowtheerror. runCatchingcalls the specified block and returns its encapsulated result if invocation was successful, catching anyThrowableexception that wasthrownfrom the block function execution and encapsulating it as a failure.
class ErrorMessage {
/**
* Throws custom error message and prints out error
* @param String message you want as an exception
*/
fun errorMessage(error: String)
{
runCatching {
println(Exception(error))
throw Exception(error)
}
}
}
- The class uses an
ErrorMessageinstance to handle error messages. - Functions like
withdrawal,deposit, andtransferfrom the classFundsContoller, perform transactional operations with error handling. So we reduce the amount of code repeated and have a function that we can call instead.
Step 4 - Hashing Class
Open Hashing.kt and reproduce the following code.
This class provides a function to hash a PIN using SHA-256.
import java.math.BigInteger
import java.security.MessageDigest
class Hashing {
/**
* Hashes supplied pin
* @param Int p
* @return String Hash
*/
fun sha256(p: Int): String {
val pinString : String = p.toString()
val md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256")
return BigInteger(1, md.digest(pinString.toByteArray())).toString(16).padStart(32, '0')
}
}
-
md.digest(pinString.toByteArray()):pinString.toByteArray(): Converts the PIN (which is a string representation of an integer) to a byte array.md.digest(byteArray): Computes the SHA-256 hash of the byte array using theMessageDigestinstance (md).
-
BigInteger(1, ...):BigInteger: Represents an arbitrary-precision integer in Kotlin.BigInteger(1, byteArray): Creates aBigIntegerfrom the provided byte array, treating it as a positive number. The1as the first argument indicates a positive gn.
-
.toString(16):- Converts the
BigIntegerto a hexadecimal string representation. The16argument specifies the radix (base) as hexadecimal.
- Converts the
-
.padStart(32, '0'):- Ensures that the resulting hexadecimal string is of length 32 characters by padding with '0' characters at the beginning if necessary.
-
Example: Password123435 -> Hash -> 63k#k4u23l@4k
Step 5 - FundsController Class
Open FundsController.kt so that you can programme the withdrawal, deposit, and transfer functions.
class FundsController {
private val e = ErrorMessage()
/**
* With draw provide amount does not put the balance below 0.
*
* Will set account balance = balance - withdrawal
* @param Object BankCustomer
* @param Double withdrawal
* @throws Exception balance less than zero
**/
fun withdrawal(bc: BankCustomer, withdrawal : Double)
{
if(withdrawal <= 0.00)
{
e.errorMessage("Withdrawal amount must be greater than 0.00")
}
if(bc.balance == 0.00)
{
e.errorMessage("Insufficient funds. Current Balance is: ${bc.balance}")
}
else if((bc.balance?.minus(withdrawal))!! >= 0.00)
{
bc.setBalance(bc.balance?.minus(withdrawal)!!)
}
else
{
e.errorMessage("Balance will be less than 0.00")
}
}
/**
* Deposits the provided amount into the account.
* @param Object BankCustomer
* @param Double deposit
* @throws Exception deposit less than zero
**/
fun deposit(bc: BankCustomer, amount : Double)
{
if(amount <= 0.00)
{
e.errorMessage("Amount being deposit must be greater than 0.00")
}
else
{
bc.setBalance(bc.balance!!.plus(amount))
}
}
/**
* Transfers amount from one acoount to another
* @param Object fromAcc
* @param Object toAcc
* @param Double amount
* @throws insufficient funds and if amount is less than 0.00
**/
fun transfer(fromAcc: BankCustomer,toAcc: BankCustomer,amount: Double)
{
if(amount <= 0.00)
{
e.errorMessage("Amount being deposit must be greater than 0.00")
}
else if(fromAcc.balance == 0.00)
{
e.errorMessage("Insufficient funds. Current Balance is: ${fromAcc.balance}")
}
else if(fromAcc.balance!!.minus(amount) >= 0.00)
{
fromAcc.setBalance(fromAcc.balance!!.minus(amount))
toAcc.setBalance(toAcc.balance!!.plus(amount))
}
else
{
e.errorMessage("Transfer cancelled balance will be less than 0.00")
}
}
}
- The class uses an
ErrorMessageinstance to handle error messages. - Functions like
withdrawal,deposit, andtransferperform the respective operations with error handling, to for theBankingCustomerclass.
Step 6 - BankCustomer Class
Open BankCustomer.kt and program the BankCustomer class. It represents a bank customer with account details, including account number, PIN, name, and balance.
import java.security.SecureRandom
class BankCustomer {
private var accNumber : Int? = null; private var pin : Int? = null; private var pinHash : String? = null
private var firstName : String? = null; private var lastName: String? = null
internal var balance : Double? = null;
/**
* @constructor initialises account, pin, and balance with 0 and first and last name as empty by invocating setBankCustomer()
* @see setBankCustomer
*/
constructor() {
setBankCustomer ( 0, 0,"","",0.0 );
}
/**
* @constructor initialises the account, pin, and balance with supplied arguments and first and last name as empty by invocating setBankCustomer()
* @param Int account
* @param Int pin
* @param Double balance
* @see setBankCustomer
*/
constructor( acc: Int, p : Int, bal: Double ) {
setBankCustomer( acc, p,"", "", bal );
}
/**
* @constructor initialises account, pin, first & last name and balance with supplied arguments by invocating setBankCustomer()
* @param Int account
* @param Int pin
* @param String first name
* @param Strng last name
* @param Double balance
* @see setBankCustomer
*/
constructor( acc : Int, p : Int, fn : String, ln : String, bal : Double ) {
setBankCustomer( acc, p, fn, ln, bal );
}
/**
* when using a constructor it initialises the object.
* @param Int accountNumber
* @param Int pin
* @param String FirstName
* @param String LastName
* @param Double Balance
*/
private fun setBankCustomer ( acc : Int, p: Int, fn : String, ln : String, bal: Double ) {
this.accNumber = acc; this.pin = p; this.pinHash = setHashOfPin(p)
this.firstName = fn; this.lastName = ln;
this.balance = bal;
}
/**
* Sets account balanace for current customer
* @param Double new balance
*/
fun setBalance(bal : Double)
{
this.balance = bal
}
/**
* Hashes the supplied pin2
* @param Int p
* @return String Hash of Pin
* @see Hashing.sha256
*/
fun setHashOfPin(p : Int): String
{
val h = Hashing()
val hash : String = h.sha256(p)
return hash
}
/**
* Gets the hash of the pib of customer supplied
* @return String Hash of Pin
*/
fun getHashOfPin(): String?
{
return this.pinHash
}
/**
* Retrieves the current customers details in a nice format
* @return String Customer Information
*/
fun customerToString() : String {
return ( "Acc No:${this.accNumber}\n Name: ${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}\n Balance: £${this.balance}\n" );
}
}
- The class has multiple constructors for flexibility in object creation.
- It includes functions to set customer name, balance, and generate a hash of the PIN.
- The
customerToStringfunction formats customer information.
Step 7 - Main Class
Open Main.kt and make the file first look like this:
This file creates instances of BankCustomer, FundsController, and ATM to simulate banking operations.
Let's create objects of the BankCustomer using each of the available constructors
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
//declaration and initialisation
var cust1 : BankCustomer = BankCustomer(12312124,1234,0.0)
var cust2 : BankCustomer = BankCustomer(12318888,1104, "First","Last",1200.00)
var cust3 : BankCustomer = BankCustomer()
println("Information for :\n\n");
printBankCustomer(cust1)
printBankCustomer(cust2)
printBankCustomer(cust3)
}
To fix the printBankCustomer() error, outside of the main() functions make a new function:
/**
* prints the object on to new lines
* @param Object BankCustomer
* @see BankCustomer.customerToString
*/
fun printBankCustomer(c: BankCustomer) {
println("${c.customerToString()}")
}
Run the program for the first time:
Information for :
Customer number:1
Acc No:12312124
Name:
Balance: £0.0
Customer number:2
Acc No:12318888
Name: First Last
Balance: £1200.0
Customer number:3
Acc No:0
Name:
Balance: £0.0
Process finished with exit code 0
- So you can see there that there are three seperate objects based on each constructor of the
BankCustomerclass. - We can control them independently.
Modify the code so that you can use the FundsController class's functons; withdrawal, transfer, and desposit.
-
Firslty, we are going to us the
withdrawalfunction:-
using the
fundsControllerobject invoke thewithdrawalfunction to withdraw10.00fromcust1, which should throw an error message for us.
-
-
Run and you should see the following:
-
Let's continue using the
fundsContollerobject to modify the balance ofcust2, with thewithdrawalfunction:fun main(args: Array<String>) { val fundsController = FundsController() //declaration and initialisation ... println("Information for :\n\n"); ... printBankCustomer(2,cust2) fundsController.withdrawal(cust2,500.00) // see cust2 after withdrawal printBankCustomer(2,cust2) // transfer money from cust2 to cust1 fundsController.transfer(cust2,cust1,500.00) // see cust2 and cust1 again.. printBankCustomer(2,cust2) printBankCustomer(1,cust1) ... } -
Run and you should see the following output:
Information for : Customer number:1 Acc No:12312124 Name: Balance: £0.0 java.lang.Exception: Insufficient funds. Current Balance is: 0.0 Customer number:2 Acc No:12318888 Name: First Last Balance: £1200.0 Customer number:2 Acc No:12318888 Name: First Last Balance: £700.0 Customer number:2 Acc No:12318888 Name: First Last Balance: £200.0 Customer number:1 Acc No:12312124 Name: Balance: £500.0 Process finished with exit code 0 -
Notice how ONLY
cust2balance has decreased by500.00to700.00 -
and second decrease from
700.00to200.00becausecust2transfered500.00tocust1 -
Remember each object is independent from each other.
Now we are going to use the ATM class to access funds again. Remember to initialise the atm object from the class after val fundsController = FundsController()
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val fundsController = FundsController()
val atm = ATM()
//declaration and initialisation
...
println("Information for :\n\n");
printBankCustomer(cust1)
fundsController.withdrawal(cust1,10.00)
}
We should utilise the pinCheck function:
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
...
fundsController.transfer(cust2,cust1,500.00)
printBankCustomer(2,cust2)
printBankCustomer(1,cust1)
println("Pin match: ${atm.checkPin(1235,cust1)}")
println("Pin match: ${atm.checkPin(1234,cust1)}")
}
If you run this again you should see at the end of terminal:
Here we can see that the atm.checkPin(1235,cust1) compares the supplied pin 1235 against the cust1 pin, by using the hashing.sha256() functions.
Lastly, you are to use atm.printBalance() and atm.getCash() functions, reproduce the below and run:
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
...
println("Pin match: ${atm.checkPin(1235,cust1)}")
println("Pin match: ${atm.checkPin(1234,cust1)}")
atm.printBalance(cust2,atm.checkPin(1104,cust2))
atm.getCash(50,cust2,atm.checkPin(1104,cust2))
atm.printBalance(cust2,atm.checkPin(1104,cust2))
printBankCustomer(2,cust2)
}
...
Customer Balanace: 200.0
Customer Balanace: 150.0
Customer number:2
Acc No:12318888
Name: First Last
Balance: £150.0
- Customer instances are created with different
constructors. - Operations like withdrawals, deposits, PIN checks, and balance checks are performed.
Step 8 : Explore
Play with the functions and classes to experiment and explore the uses. Try and modifiy the classes to do more functionality:
- BankCustomer
-
setBankCustomerName()- This will set the first and last name of the customer
- needs to arguments, fN and ln both of which are strings.
-
makeAccountNumber()-
This should create an account number, use
Random()to generate 8 random numbers from 0 to 8. Whereby the first number cannont be a 0. -
Code: Suggested Solution
/** * Creates an account number using repeat and random. */ fun makeAccountNumber() { var tmpAccNumber : String? = null repeat(8){ var tmpNum = Random.nextInt(0, 9) // Avoid 0 as the first number. while (it == 0 && tmpNum == 0) { tmpNum = Random.nextInt(0, 9) } if(it == 0) { tmpAccNumber = tmpNum.toString() } else { tmpAccNumber += tmpNum.toString() } } this.accNumber = tmpAccNumber?.toInt() }
-
-
makeSortCode()Code: Suggested Solution
/** * Creates an account number using repeat and random. * * Format: xx-xx-xx */ fun makeSortCode() { var tmpSortCode : String = "" repeat(6){ if (it != 0 && it % 2 == 0) { tmpSortCode += '-' } tmpSortCode += Random.nextInt(0, 6).toString() } this.sortCode = tmpSortCode }Output
Customer number:2 Sort Code: 00-01-12 Acc No: 53044760 Name: First Last Balance: £150.0- You need to create a
sortCodevariable and modify thecustomerToString()functions to print thesortCode
</div> </details>- Make a new class for a Card so that each bank customer can have one, with a card number, expiry date, and cvv for each
cust.- Card number format
-
Visa cards:
-
Digit 1: identifies as visa
-
Digits 2 – 6: Make up the bank/sort number
-
Digits 7 – 12 or 7 – 15: Represent the account number
-
Digits 13 or 16: Is a check digit
- See http://datagenetics.com/blog/july42013/index.html
-
Code: Suggested Solution
```kt class Card { private var card : String? = null private var name : String? = null private var expiryDate : String? = null private var cvv : Int? = null fun createCard(c:BankCustomer) { /* Visa cards: Digit 1: identifies as visa Digits 2 – 6: Make up the bank/sort number Digits 7 – 12 or 7 – 15: Represent the account number Digits 13 or 16: Is a check digit */ var tmpCardNumber : String ="4" var tmpSortCode : String? = c.getSortCode() if (tmpSortCode != null) { tmpCardNumber += tmpSortCode.replace("-", "") } tmpCardNumber += c.getAccount() tmpCardNumber += checkDigit(tmpCardNumber) this.card = tmpCardNumber this.cvv = cvvGenterator() this.expiryDate = generateRandomExpiryDate() this.name = c.getName() } /** * Calculates and returns the Luhn Algorithm check digit for a given partial card number. * * The Luhn Algorithm is used to validate credit card numbers. * * See: http://datagenetics.com/blog/july42013/index.html * * @param partial The partial card number (without the check digit). * @return The calculated check digit. * */ fun checkDigit(partial: String?): Int { var checkSum = 0 if (partial != null) { for (p in 0 until partial.length) { val digit = partial[p].toString().toInt() if (p % 2 == 0) { // For even-indexed digits, add them directly to the sum checkSum += digit } else { // For odd-indexed digits, double the digit and add the digits of the result to the sum val doubled = digit * 2 checkSum += if (doubled > 9) doubled - 9 else doubled } } } // Calculate the check digit by finding the remainder when the sum is divided by 10 // and then subtracting the result from 10. return (10 - (checkSum % 10)) % 10 } /** * Generate 3 digits for cvv * @return Int CVV */ fun cvvGenterator() : Int { return Random.nextInt(100, 999) } /** * Generates a random MM/YYYY expiry date for a credit card. * * The generated date is within the next 10 years from the current year. * * @return The formatted expiry date as MM/YYYY. */ fun generateRandomExpiryDate(): String { val currentYear = Calendar.getInstance().get(Calendar.YEAR) val randomYear = currentYear + Random.nextInt(10) // Generating a random year within the next 10 years val randomMonth = Random.nextInt(12) + 1 // Generating a random month (1-12) // Formatting the date as MM/YYYY return String.format("%02d/%d", randomMonth, randomYear) } fun printDetails() : String { return "Name: ${this.name}\nCard No: ${this.card}\n Expiry Date: ${this.expiryDate}\nCVV: ${this.cvv}" } } ```
-
All code for the lab
Full code: Main.kt [44 lines]
fun main(args: Array<String>) { val fundsController = FundsController() val atm = ATM() //declaration and initialisation var cust1 : BankCustomer = BankCustomer(12312124,1234,0.0) var cust2 : BankCustomer = BankCustomer(12318888,1104, "First","Last",1200.00) var cust3 : BankCustomer = BankCustomer() // View the BankCustomer objects println("Information for :\n"); printBankCustomer(1,cust1) fundsController.withdrawal(cust1,10.00) printBankCustomer(2,cust2) fundsController.withdrawal(cust2,500.00) printBankCustomer(2,cust2) fundsController.transfer(cust2,cust1,500.00) printBankCustomer(2,cust2) printBankCustomer(1,cust1) println("Pin match: ${atm.checkPin(1235,cust1)}") println("Pin match: ${atm.checkPin(1234,cust1)}") atm.printBalance(cust2,atm.checkPin(1104,cust2)) atm.getCash(50,cust2,atm.checkPin(1104,cust2)) atm.printBalance(cust2,atm.checkPin(1104,cust2)) printBankCustomer(2,cust2) val card1 = Card() card1.createCard(cust2) println(card1.printDetails()) } /** * prints the object on to new lines * @param Object BankCustomer * @see BankCustomer.customerToString */ fun printBankCustomer(n:Int , c: BankCustomer) { println("Customer number:${n} \n ${c.customerToString()}") }Full code: BankCustomer.kt [162 lines]
import java.security.SecureRandom import kotlin.random.Random class BankCustomer { private var accNumber : Int? = null; private var pin : Int? = null; private var pinHash : String? = null private var firstName : String? = null; private var lastName: String? = null internal var balance : Double? = null; private var sortCode : String? = null /** * @constructor initialises account, pin, and balance with 0 and first and last name as empty by invocating setBankCustomer() * @see setBankCustomer */ constructor() { setBankCustomer ( 0, 0,"","",0.0 ); } /** * @constructor initialises the account, pin, and balance with supplied arguments and first and last name as empty by invocating setBankCustomer() * @param Int account * @param Int pin * @param Double balance * @see setBankCustomer */ constructor( acc: Int, p : Int, bal: Double ) { setBankCustomer( acc, p,"", "", bal ); } /** * @constructor initialises account, pin, first & last name and balance with supplied arguments by invocating setBankCustomer() * @param Int account * @param Int pin * @param String first name * @param Strng last name * @param Double balance * @see setBankCustomer */ constructor( acc : Int, p : Int, fn : String, ln : String, bal : Double ) { setBankCustomer( acc, p, fn, ln, bal ); } /** * when using a constructor it initialises the object. * @param Int accountNumber * @param Int pin * @param String FirstName * @param String LastName * @param Double Balance */ private fun setBankCustomer ( acc : Int, p: Int, fn : String, ln : String, bal: Double ) { makeAccountNumber(); makeSortCode(); this.pin = p; this.pinHash = setHashOfPin(p) this.firstName = fn; this.lastName = ln; this.balance = bal; } /** * Get the first and lastname * @return String */ fun getName() : String { return "${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}" } /** * Sets account balanace for current customer * @param Double new balance */ fun setBalance(bal : Double) { this.balance = bal } /** * Hashes the supplied pin2 * @param Int p * @return String Hash of Pin * @see Hashing.sha256 */ fun setHashOfPin(p : Int): String { val h = Hashing() val hash : String = h.sha256(p) return hash } /** * Gets the hash of the pib of customer supplied * @return String Hash of Pin */ fun getHashOfPin(): String? { return this.pinHash } /** * Get account number * @return Int accNumber */ fun getAccount() : Int? { return this.accNumber } /** * Get sort number * @return String sortCode */ fun getSortCode() : String? { return this.sortCode } /** * Retrieves the current customers details in a nice format * @return String Customer Information */ fun customerToString() : String { return ("\n Sort Code: ${this.sortCode}\n Acc No:${this.accNumber}\n Name: ${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}\n Balance: £${this.balance}\n" ); } /** * Creates an account number using repeat and random. * * Format: xxxxxxxx */ fun makeAccountNumber() { var tmpAccNumber : String? = null repeat(8){ var tmpNum = Random.nextInt(0, 9) // Avoid 0 as the first number. while (it == 0 && tmpNum == 0) { tmpNum = Random.nextInt(0, 9) } if(it == 0) { tmpAccNumber = tmpNum.toString() } else { tmpAccNumber += tmpNum.toString() } } this.accNumber = tmpAccNumber?.toInt() } /** * Creates an account number using repeat and random. * * Format: xx-xx-xx */ fun makeSortCode() { var tmpSortCode : String = "" repeat(6){ if (it != 0 && it % 2 == 0) { tmpSortCode += '-' } tmpSortCode += Random.nextInt(0, 6).toString() } this.sortCode = tmpSortCode } }Full code: Hashing.kt [14 lines]
import java.math.BigInteger import java.security.MessageDigest class Hashing { /** * Hashes supplied pin * @param Int p * @return String Hash */ fun sha256(p: Int): String { val pinString : String = p.toString() val md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256") return BigInteger(1, md.digest(pinString.toByteArray())).toString(16).padStart(32, '0') } }Full code: FundsController.kt [77 lines]
class FundsController { private val e = ErrorMessage() /** * With draw provide amount does not put the balance below 0. * * Will set account balance = balance - withdrawal * @param Object BankCustomer * @param Double withdrawal * @throws Exception balance less than zero **/ fun withdrawal(bc: BankCustomer, withdrawal : Double) { if(withdrawal <= 0.00) { e.errorMessage("Withdrawal amount must be greater than 0.00") } if(bc.balance == 0.00) { e.errorMessage("Insufficient funds. Current Balance is: ${bc.balance}") } else if((bc.balance?.minus(withdrawal))!! >= 0.00) { bc.setBalance(bc.balance?.minus(withdrawal)!!) } else { e.errorMessage("Balance will be less than 0.00") } } /** * Deposits the provided amount into the account. * @param Object BankCustomer * @param Double deposit * @throws Exception deposit less than zero **/ fun deposit(bc: BankCustomer, amount : Double) { if(amount <= 0.00) { e.errorMessage("Amount being deposit must be greater than 0.00") } else { bc.setBalance(bc.balance!!.plus(amount)) } } /** * Transfers amount from one acoount to another * @param Object fromAcc * @param Object toAcc * @param Double amount * @throws insufficient funds and if amount is less than 0.00 **/ fun transfer(fromAcc: BankCustomer,toAcc: BankCustomer,amount: Double) { if(amount <= 0.00) { e.errorMessage("Amount being deposit must be greater than 0.00") } else if(fromAcc.balance == 0.00) { e.errorMessage("Insufficient funds. Current Balance is: ${fromAcc.balance}") } else if(fromAcc.balance!!.minus(amount) >= 0.00) { fromAcc.setBalance(fromAcc.balance!!.minus(amount)) toAcc.setBalance(toAcc.balance!!.plus(amount)) } else { e.errorMessage("Transfer cancelled balance will be less than 0.00") } } }Full code: ErrorMessage.kt [13 lines]
class ErrorMessage { /** * Throws custom error message and prints out error * @param String message you want as an exception */ fun errorMessage(error: String) { runCatching { println(Exception(error)) throw Exception(error) } } }Full code: ATM.kt [66 lines]
import javax.swing.text.StyledEditorKit.BoldAction /** * */ class ATM { private val e = ErrorMessage() private val fc = FundsController() /** * checkPin to see if it is correct * @param Int checkPin * @param Object BankCustomer * @return Boolean */ fun checkPin(p : Int, c: BankCustomer) : Boolean { val h = Hashing() var match : Boolean = false match = h.sha256(p) == c.getHashOfPin() return match } /** * * @param Object BankCustomer * @param Boolean m * @return String * @see BankCustomer.balance */ fun printBalance(c: BankCustomer,m : Boolean) { if( m == true) { println("Customer Balanace: ${c.balance}") } else { e.errorMessage("Incorrect Pin Supplied") } } /** * Withdraws cash from ATM, based on available funds * @param Int Amount * @param Object BankCustomer * @param Boolean ATM.checkPin * @return String * @throws Exception balance less than zero * @see FundsController.withdrawal * @see ATM.checkPin */ fun getCash(amount : Int, c: BankCustomer, m : Boolean) { if( m == true) { fc.withdrawal(c,amount.toDouble()) } else { e.errorMessage("Incorrect Pin Supplied") } } }Full code: Card.kt [104 lines]
import java.text.DateFormat import java.util.* import javax.print.DocFlavor.STRING import kotlin.random.Random class Card { private var card : String? = null private var name : String? = null private var expiryDate : String? = null private var cvv : Int? = null fun createCard(c:BankCustomer) { /* Visa cards: Digit 1: identifies as visa Digits 2 – 6: Make up the bank/sort number Digits 7 – 12 or 7 – 15: Represent the account number Digits 13 or 16: Is a check digit */ var tmpCardNumber : String ="4" var tmpSortCode : String? = c.getSortCode() if (tmpSortCode != null) { tmpCardNumber += tmpSortCode.replace("-", "") } tmpCardNumber += c.getAccount() tmpCardNumber += checkDigit(tmpCardNumber) this.card = tmpCardNumber this.cvv = cvvGenterator() this.expiryDate = generateRandomExpiryDate() this.name = c.getName() } /** * Calculates and returns the Luhn Algorithm check digit for a given partial card number. * * The Luhn Algorithm is used to validate credit card numbers. * * See: http://datagenetics.com/blog/july42013/index.html * * @param partial The partial card number (without the check digit). * @return The calculated check digit. * */ fun checkDigit(partial: String?): Int { var checkSum = 0 if (partial != null) { for (p in 0 until partial.length) { val digit = partial[p].toString().toInt() if (p % 2 == 0) { // For even-indexed digits, add them directly to the sum checkSum += digit } else { // For odd-indexed digits, double the digit and add the digits of the result to the sum val doubled = digit * 2 checkSum += if (doubled > 9) doubled - 9 else doubled } } } // Calculate the check digit by finding the remainder when the sum is divided by 10 // and then subtracting the result from 10. return (10 - (checkSum % 10)) % 10 } /** * Generate 3 digits for cvv * @return Int CVV */ fun cvvGenterator() : Int { return Random.nextInt(100, 999) } /** * Generates a random MM/YYYY expiry date for a credit card. * * The generated date is within the next 10 years from the current year. * * @return The formatted expiry date as MM/YYYY. */ fun generateRandomExpiryDate(): String { val currentYear = Calendar.getInstance().get(Calendar.YEAR) val randomYear = currentYear + Random.nextInt(10) // Generating a random year within the next 10 years val randomMonth = Random.nextInt(12) + 1 // Generating a random month (1-12) // Formatting the date as MM/YYYY return String.format("%02d/%d", randomMonth, randomYear) } fun printDetails() : String { return "Name: ${this.name}\nCard No: ${this.card}\n Expiry Date: ${this.expiryDate}\nCVV: ${this.cvv}" } } - You need to create a
-