Lab 8.1: OOP with Data Storage
Introduction
In this lab you are going to utilise what you have learnt about Object Oriented Program, methods, error handling, XML, JSON and CSV.
Remember that when you see ... in a code block it means code before or after is not shown for readability.
In this lab you will write 414 lines of code.
Step 1: Initialise the Project
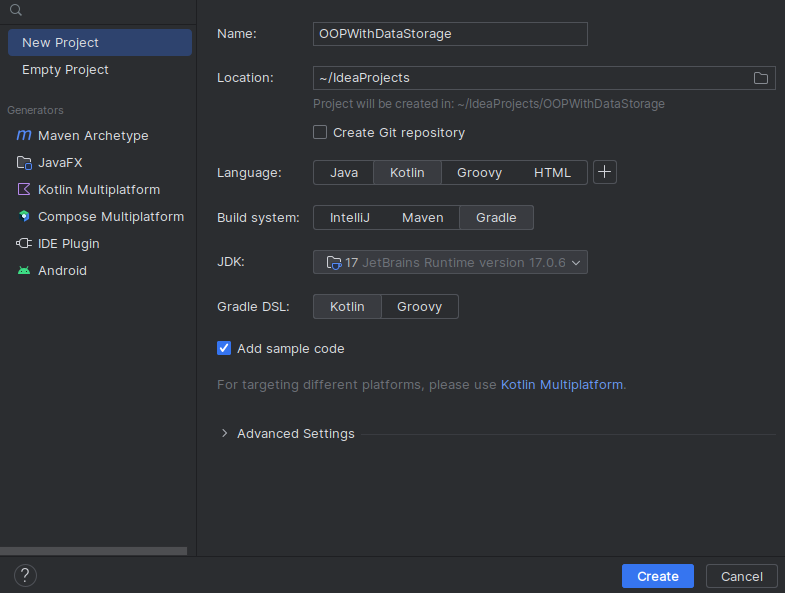
- Launch a new IntelliJ project and give it an appropriate name
- Select
Kotlinas the Language - Select
Gradleas the Build system
-
Make these files in the directory
src/main/kotlin:BankCustomerClass (Kotlin Class/File)DataUtils.ktFile (Kotlin Class/File)MyMutuableExtensionsObject (Kotlin Class/File)
-
Make these files in
src:customers.csvFile (File)customers.jsonFile (File)customers.xmlFile (File)

Step 2: BankCustomer Class Part 1
We are using the some of the BankCustomer code we had from Lab 10.
-
Reproduce the following as is:
/** * Represents a bank customer with basic information such as first name, last name, PIN, account number, * and sort code. * * @property firstName The first name of the customer. * @property lastName The last name of the customer. * @property pin The PIN (Personal Identification Number) of the customer. * @property account The account number of the customer. * @property sortCode The sort code associated with the customer's account. * * @constructor Creates a new [BankCustomer] with the specified details. * @param fn The first name of the customer. * @param ln The last name of the customer. * @param p The PIN (Personal Identification Number) of the customer. * @param acc The account number of the customer. * @param sc The sort code associated with the customer's account. */ class BankCustomer { var firstName: String? = null var lastName: String? = null var pin: Int? = null var account: String? = null var sortCode: String? = null /** * Default constructor for [BankCustomer]. */ constructor() /** * Creates a new [BankCustomer] with the specified details. * * @param fn The first name of the customer. * @param ln The last name of the customer. * @param p The PIN (Personal Identification Number) of the customer. * @param acc The account number of the customer. * @param sc The sort code associated with the customer's account. */ constructor(fn: String, ln: String, p: Int, acc: String, sc: String) { firstName = fn lastName = ln pin = p account = acc sortCode = sc } /** * Prints the details of the customer, including name, PIN, account number, and sort code. */ fun printMe() { println( "Customer:\n\tName: ${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}\n\tPin: ${this.pin}\n\t" + "Account: ${this.account}\n\tSort Code:${this.sortCode}" ) } }
Step 3: Main class Part 1
-
Open the
Main.ktfile and modify the contents to look like this: -
We are going to initialise three bankCustomers, the two you see below and one more of your choice.
Step 4: build.gradle.kts Part 1
-
Open the
build.gradle.ktsfile located in the project view just under thetest\folder. -
Navigate to the
dependicessections and add the following code to import the CSV library usingimplementation("com.opencsv:opencsv:3.7")into the project;
Step 5: DataUtils.tk Part 1
We are now going to create functionality to read and write to a CSV, our fist type of data storage file.
-
Open the
DataUtils.ktfile -
Reproduce the following code:
import com.opencsv.CSVReaderBuilder // implementation("com.opencsv:opencsv:3.7") import com.opencsv.CSVWriter // implementation("com.opencsv:opencsv:3.7") import java.io.File // for writing and reading from a file. /** * Utility object for handling data operations, including loading and writing data in JSON, CSV, and XML formats. */ object DataUtils { /** * Loads a list of [BankCustomer] objects from a CSV file. * * @param filePath The path to the CSV file. * @return A [MutableList] of [BankCustomer] objects loaded from the CSV file. */ fun loadCustomersFromCSV(filePath: String): MutableList<BankCustomer> { val file = File(filePath) // create file if needed makeFile(filePath) if (file.exists()) { file.reader().use { reader -> try { val csvReader = CSVReaderBuilder(reader).build() val lines = csvReader.readAll() val customerList = mutableListOf<BankCustomer>() for (line in lines) { // Create BankCustomer objects from CSV lines // for each column in a a line[#] val customer = BankCustomer(line[0], line[1], line[2].toInt(), line[3], line[4]) // add customer to the list of BankCustomers customerList.add(customer) } // once finished return the list return customerList } catch (e: Exception) { // Handle exceptions during CSV parsing // return and empty list if fails return mutableListOf() } } } else { // return and empty list if all fails return mutableListOf() } } /** * Writes a list of [BankCustomer] objects to a CSV file. * * @param customerList The list of [BankCustomer] objects to be written to the CSV file. * @param filePath The path to the CSV file. */ fun writeCustomersToCSV(customerList: List<BankCustomer>, filePath: String) { val file = File(filePath) // create file if needed makeFile(filePath) if (file.exists()) { file.writer().use { writer -> val csvWriter = CSVWriter(writer) for (customer in customerList) { // Convert BankCustomer objects to CSV records val record = arrayOf( customer.firstName.orEmpty(), customer.lastName.orEmpty(), customer.pin?.toString() ?: "", customer.account.orEmpty(), customer.sortCode.orEmpty() ) csvWriter.writeNext(record) } csvWriter.close() } } else { println("File doesn't exist") } } /** * Creates a new file at the specified [filePath]. * * @param filePath The path to the file to be created. */ fun makeFile(filePath: String) { val file = File(filePath) try { if (file.createNewFile()) { println("File created successfully.") } else { println("File already exists.") } } catch (e: Exception) { // Handle exceptions during file creation println("An error occurred while creating the file: ${e.message}") } } }
Remember each KDoc you create provides helper inforamtion when you hover over each function/method.
Step 6: MyMutuableExtensions.kt
We are going to create some extension methods for the MutuableList class. Sometimes for example we need to extra features where sometimes you don't want to add duplicates by mistake.
-
Open the
MyMutuableExtensions -
Reproduce the follwing code:
/** * Extension functions for [MutableList] of [BankCustomer] to perform various operations. */ object MyMutableExtensions { /** * Removes duplicate [BankCustomer] objects based on their account numbers. * * @return A new [MutableList] containing distinct [BankCustomer] objects based on account numbers. */ fun MutableList<BankCustomer>.removeDuplicatesByAccountNumber() : MutableList<BankCustomer>{ return this.distinctBy { it.account }.toMutableList() } /** * Adds a [BankCustomer] to the [MutableList] only if a customer with the same account number * does not already exist in the list. * * @param customer The [BankCustomer] to be added. */ fun MutableList<BankCustomer>.addIfNotDuplicate(customer: BankCustomer) { if (this.all { it.account != customer.account }) { this.add(customer) } } /** * Extension function to remove a [BankCustomer] from the [MutableList] based on the account number. * * @param accountNumber The account number of the customer to be removed. */ fun MutableList<BankCustomer>.removeByAccountNumber(accountNumber: String?) { val customerToRemove = this.find { it.account == accountNumber } if (customerToRemove != null) { this.remove(customerToRemove) println("Customer with account number $accountNumber removed successfully.") } else { println("No customer found with account number $accountNumber. No customer removed.") } } /** * Prints details of all [BankCustomer] objects in the [MutableList]. */ fun MutableList<BankCustomer>.printAll() { this.forEach { customer -> customer.printMe() } } /** * Prints details of [customer] object in the [MutableList] of [BankCustomer]s . */ fun MutableList<BankCustomer>.printOne(acc:String) { for ((index, customer) in this.withIndex()) { if (customer.account == acc) { customer.printMe() } else { println("Error: ${acc} not found") } } } }
Step 7: Main.kt Part 2
-
ReOpen the
Main.ktand modify the top of the file so we can import the our code:// MyMutableExtensions file import MyMutableExtensions.addIfNotDuplicate import MyMutableExtensions.printAll import MyMutableExtensions.removeByAccountNumber import MyMutableExtensions.removeDuplicatesByAccountNumber // DataUtils file import DataUtils.loadCustomersFromCSV import DataUtils.writeCustomersToCSV fun main(args: Array<String>){ ... } -
Now lets use some of these functions and methods we have now imported to write and read unique values to/from the a
customers.csv.... fun main(args: Array<String>){ // Load the content of the customers.csv as a [MutuableList] of [BankCustomers] var csvExistingCustomers = loadCustomersFromCSV("customers.csv") // add the first two customers using the built-in MutuableList.add method. csvExistingCustomers.add(newCustomer) csvExistingCustomers.add(customer) println("All Customers:") // print all the customers using the print function println(csvExistingCustomers) // and again using our own extension for the MutuableList csvExistingCustomers.printAll() // Now write the csvExisitingCusomters to a the customers.csv writeCustomersToCSV(csvExistingCustomers,"customers.csv") } -
Run the program, and you should see a very similar output:
File already exists. [BankCustomer@4cb2c100, BankCustomer@6fb554cc] All Customers: Customer: Name: Jane Doe Pin: 5678 Account: 987654321 Sort Code:123456 Customer: Name: Marshall Mathers Pin: 5678 Account: 123456789 Sort Code:123456 -
Check in the
customers.csvto see the output ofwriteCustomersToCSV(csvExistingCustomers,"customers.csv").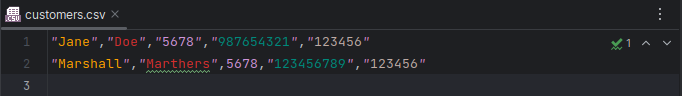
-
Modify the first the line
csvExistingCustomers.add(newCustomer)inMain.ktto use our add method:... fun main(args: Array<String>){ // Load the content of the customers.csv as a [MutuableList] of [BankCustomers] var csvExistingCustomers = loadCustomersFromCSV("customers.csv") // add the first customers using our MutuableList.addIfNotDuplicate() method. csvExistingCustomers.addIfNotDuplicate(newCustomer) / add the second customer using the built-in MutuableList.add method. csvExistingCustomers.add(customer) ... } -
Run again and you should see the following:
File already exists. All Customers: [BankCustomer@4cb2c100, BankCustomer@6fb554cc, BankCustomer@614c5515] Customer: Name: Jane Doe Pin: 5678 Account: 987654321 Sort Code:123456 Customer: Name: Marshall Marthers Pin: 5678 Account: 123456789 Sort Code:123456 Customer: Name: Marshall Mathers Pin: 5678 Account: 123456789 Sort Code:123456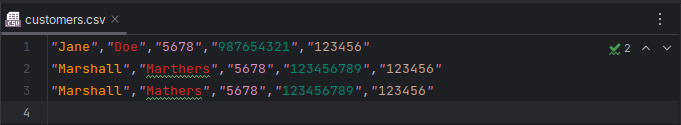
- You will see that the
Jane Doe, has not been duplicated because we used ouraddIfNotDuplicate()that does not duplicate based on account number. However,add()does not have this functionality by default.
- You will see that the
-
To remove any duplicates we can use the exentsion we made
removeDuplicatesByAccountNumber()and we will also replace theadd()for the second customer:... fun main(args: Array<String>){ // Load the content of the customers.csv as a [MutuableList] of [BankCustomers] var csvExistingCustomers = loadCustomersFromCSV("customers.csv") // remove duplicates in the list read from the `customers.csv` csvExistingCustomers = csvExistingCustomers.removeDuplicatesByAccountNumber() // add the first customers using our MutuableList.addIfNotDuplicate() method. csvExistingCustomers.addIfNotDuplicate(newCustomer) / add the second customer using the built-in MutuableList.add method. csvExistingCustomers.addIfNotDuplicate(customer) ... } -
Now run again and you should only have the two customers in your
customers.csvnow
Step 8: Storage using JSON
-
ReOpen the
build.gradle.ktsand add the following,implementation("com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.9"), to the dependicies section so we can utilise a library for reading and writing a JSON: -
ReOpen the
DataUtils.ktand modify the top of the file to includeimport com.google.gson.Gson -
Navigate to the end of
writeCustomersToCSV(...)and still inside theobject DataUtils{reproduce the following code. We using theGson()Class that we imported to load (read) and write the theBankCustomerslist from/tocustomers.json:... fun writeCustomersToCSV(customerList: List<BankCustomer>, filePath: String) { ... } /** * Loads a list of [BankCustomer] objects from a JSON file. * * @param filePath The path to the JSON file. * @return A [MutableList] of [BankCustomer] objects loaded from the JSON file. */ fun loadCustomersFromJSON(filePath: String): MutableList<BankCustomer> { val gson = Gson() val file = File(filePath) if (file.exists()) { file.reader().use { reader -> try { // Deserialize JSON into a list of BankCustomer objects return gson.fromJson(reader, Array<BankCustomer>::class.java).toMutableList() } catch (e: Exception) { // Handle exceptions during JSON parsing return mutableListOf() } } } else { // If the file does not exist, return an empty list return mutableListOf() } } /** * Writes a list of [BankCustomer] objects to a JSON file. * * @param customerList The list of [BankCustomer] objects to be written to the JSON file. * @param filePath The path to the JSON file. */ fun writeCustomersToJSON(customerList: List<BankCustomer>, filePath: String) { val gson = Gson() val file = File(filePath) if (file.exists()) { // Convert the updated list to a formatted JSON string // Convert the list to a JSON string with each property on a new line val formattedJson = gson.toJson(customerList) // Write the formatted JSON to the file (overwrite) file.writer().use { writer -> writer.write(formattedJson) } } else { println("File doesn't exist") } } -
Modifty
Main.ktso that we can store data in a JSON format. We will also need to import from outDataUtils.ktat the top of the file like last time: -
We are essentially repeating what we did last time for the CSV but using the JSON functionality we have written:
... fun main(args: <String>){ ... //CSV ... writeCustomersToCSV(csvExistingCustomers,"customers.csv") //JSON var jsonExistingCustomers = loadCustomersFromJSON("customers.json") jsonExistingCustomers = jsonExistingCustomers.removeDuplicatesByAccountNumber() jsonExistingCustomers.addIfNotDuplicate(newCustomer) jsonExistingCustomers.addIfNotDuplicate(customer) writeCustomersToJSON(jsonExistingCustomers,"customers.json") } -
Run and check the
customers.jsonand see that you have one long line:[{"firstName":"Jane","lastName":"Doe","pin":5678,"account":"987654321","sortCode":"123456"},{"firstName":"Steph","lastName":"Jupe","pin":5678,"account":"123456789","sortCode":"123456"}]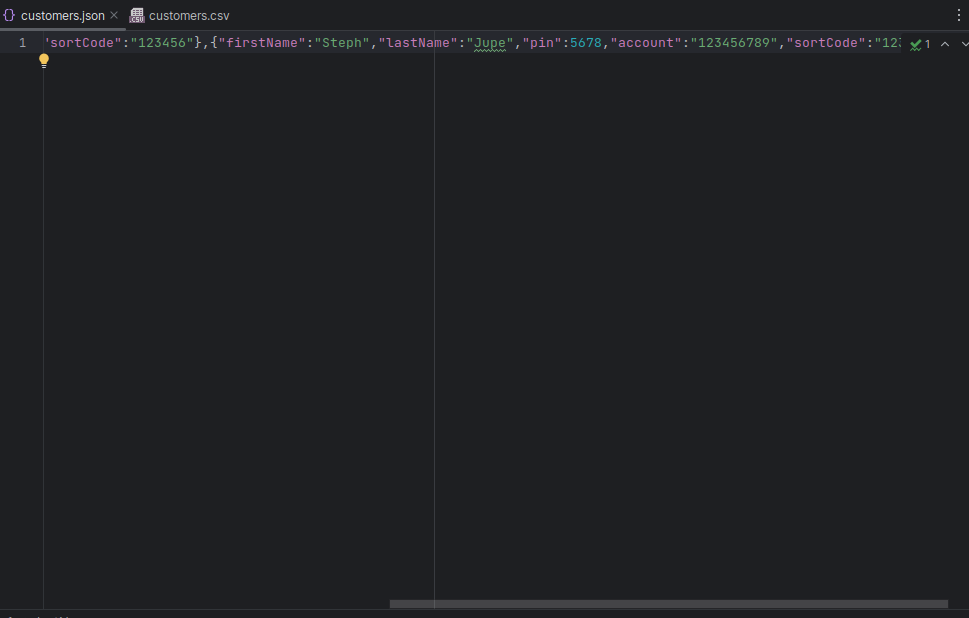
-
Modify the
DataUtils.ktso that we can have a more human readable version of thecustomers.json:... fun writeCustomersToJSON(customerList: List<BankCustomer>, filePath: String) { val gson = Gson() ... val formattedJson = gson.toJson(customerList) .replace("[", "[\n\t") .replace(",", ",\n\t\t") .replace("{", "{\n\t\t") .replace("}", "\n\t}") .replace("},\n\t\t{", "},\n\t{") .replace("]", "\n]") ... }.replace("old", "new"), so we for the most part we are getting a new line\nand a tab\tappended to each brace[{}]and comma,.
-
Run again and see the difference in the
customers.json
Step 9: XML Storage
This step is a little more involved than the previous two storage options.
-
ReOpen the
build.gradle.ktsso that the XML libraries can be installed: -
Now we are going to map our
BankCustomerClass by implementing@XmlRootElement(name = "customer")and importingimport javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElementin theBankCusotmer.ktfile. Make sure to reproduce as shown below: -
Then navigate to
DataUtils.ktand add the imports for XML functionality at the top of the file like the other imports: -
Now we can add the write and load functions for the XML in the
DataUtils.kt, navigate to the endwriteCustomersToJSON(...)and between that and themakeFile(...)function add the followingloadCustomersFromXml()andwriteCustomersToXml()as seen below:... fun writeCustomersToJSON(customerList: List<BankCustomer>, filePath: String) { ... } /** * Loads a list of [BankCustomer] objects from an XML file. * * @param filePath The path to the XML file. * @return A [MutableList] of [BankCustomer] objects. */ fun loadCustomersFromXml(filePath: String): MutableList<BankCustomer> { try { val context = JAXBContext.newInstance(CustomersWrapper::class.java) val unmarshaller = context.createUnmarshaller() val wrapper = unmarshaller.unmarshal(File(filePath)) as CustomersWrapper return wrapper.customerList.toMutableList() } catch (e: Exception) { // Handle exceptions during XML parsing e.printStackTrace() } return mutableListOf() } /** * Writes a list of [BankCustomer] objects to an XML file. * * @param customers The list of [BankCustomer] objects to write. * @param filePath The path to the XML file. * @throws Exception to log */ fun writeCustomersToXml(customers: List<BankCustomer>, filePath: String) { try { val context = JAXBContext.newInstance(CustomersWrapper::class.java) val marshaller = context.createMarshaller() marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true) val wrapper = CustomersWrapper() wrapper.customerList = ArrayList(customers) marshaller.marshal(wrapper, File(filePath)) } catch (e: Exception) { // Handle exceptions during XML writing e.printStackTrace() } } /** ... */ fun makeFile(filePath: String) { ... } -
At the end of the
object DataUtils{...}or if you like the very end of theDataUtils.ktadd the followingCustomersWrapperWrapperclass:object DataUtils { /** ... */ fun makeFile(filePath: String) { ... } } /** * Wrapper class for marshalling and unmarshalling a list of [BankCustomer] objects. */ @XmlRootElement(name = "customersWrapper") @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) class CustomersWrapper { @XmlElement(name = "customer") var customerList: List<BankCustomer> = ArrayList() } -
Now we need to modify
Main.ktto use the load and write XML functions we have made. Firstly, add reference to the new xml functions we have in theDataUtils.kt: -
Modify the code inside
main(args : <String>)so that the functionswriteCustomersToXmlandloadCustomersToXml. Navigate to the end ofmain(...):fun main(arg: <String>){ ... writeCustomersToJSON(jsonExistingCustomers,"customers.json") ... // XML var existingCustomers = loadCustomersFromXml("customers.xml") existingCustomers = existingCustomers.removeDuplicatesByAccountNumber() // Add the new customer to the existing list existingCustomers.addIfNotDuplicate(newCustomer) existingCustomers.addIfNotDuplicate(customer) println("All Customers:") existingCustomers.printAll() // Write the updated list back to XML writeCustomersToXml(existingCustomers, "customers.xml") } -
Run the code, and your
customers.xmlfile should look like: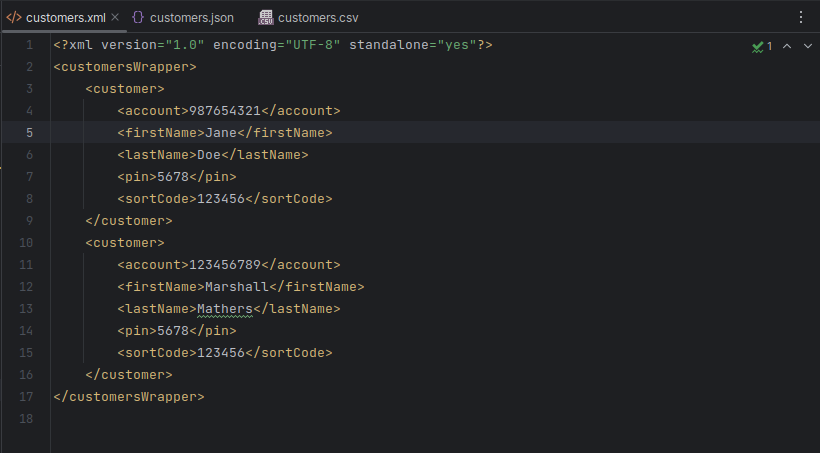
Step 10: More
-
The third customer you made at the beginning can be added to all three files. Try and do this now.
-
Try removing a record by first using the mutable extension method we made but have not used yet to remove the
customerwhose name isMarshal Mathers, for example: -
Now that the
existingCustomerhas that customer removed try using thewriteCustomersTo<XML/JSON/CSV>(...)... which ever one you used and see the change in the file.
Completed project
You can download the completed project from here as a zip, if you have not completed the lab or just want to explore and play with as is: