ADC to PWM functionality
-
You need to have finished:
Updating the PWM library
We need to add the a new prototype to the bbb_pwm.h and the body to the bbb_pwm.c files, that converts the ADC value to a the correct PWM duty cycle against the specified period.
-
Remember that the Beaglebone blacks ADC chip does not use 8bit levels, i.e 0-255 like you would find on a Atmel328p.
-
It uses provides the duty cycle as % of the period.
-
Open the
bbb_pwm.hfile and modify to include the prototype below calledmap: -
To map we need to get the relationship between adc and the period to get the duty cycle
\[ \text{duty_cycle_ns} = \frac{\text{adc_value} \cdot \text{period_ns}}{4095} \]
-
We now can implement above equation by modifying the
bbb_pwm.cfile to include the body of the previously defined prototype, place the function at the bottom of the file:Suppressed code here [15 lines]
... // Map ADC value to PWM duty cycle with user-specified period unsigned int map(u_int16_t adc_value, unsigned int period_ns) { if (adc_value > 4095) { fprintf(stderr, "ADC value out of range\n"); return 1; } // Map ADC value (0 to 4095) to PWM duty cycle (0 to period_ns) unsigned int duty_cycle_ns = (adc_value * period_ns) / 4095; return duty_cycle_ns; } -
As the
Makefilealready exists and does not need updating, simply remake the library:
Implementing an example
We are going to create a script that utlises what we did for ~/examples_C/adc_read.c and examples_C/pwm_test.c, by utilising both libraries bbb_pwm.h and bbb_adc.h.
-
Create a new directory in the
homedirectory and call it~/examples_C/adc2pwmand inside a file calledadc2pwm.c -
Modify the contents of
adc2pwm.cwith the following code:Suppressed code here [61 lines]
#include <bbb_pwm.h> #include <bbb_adc.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdint.h> int main() { PWM pwm; unsigned int adc_reading = 0; unsigned int user_defined_period_ns = 1000000; unsigned int duty_cycle = 0; // Initialize PWM on a specified pin, for example "P9_14" pwm_init(&pwm, "P9_14"); // Set initial PWM period pwm_set_period(&pwm, user_defined_period_ns); // Enable PWM output pwm_enable(&pwm); printf("Phy: %s\nChannel: %s\nChip: %s\nPeriod path: %s\nDuty Cycle path: %s\nEnable path: %s\n", pwm.phy_pin, pwm.channel, pwm.chip, pwm.period_path, pwm.duty_cycle_path, pwm.enable_path); // Loop to read ADC values and update PWM duty cycle for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) { adc_get_value(0, &adc_reading); // Read ADC value from channel 0 printf("ADC Reading: %u\n", adc_reading); // Map the ADC reading to the PWM duty cycle and update it duty_cycle = map(adc_reading, user_defined_period_ns); pwm_set_duty_cycle(&pwm, duty_cycle); sleep(1); // Update every 1 second } // Disable PWM and clean up pwm_disable(&pwm); pwm_cleanup(&pwm); return 0; } -
Remember to create a
Makefilefile:Suppressed code here [25 lines]
# Compiler and flags CC = gcc CFLAGS = -Wall -Werror # Target executable name TARGET = adc2pwm # Source files SRC = adc2pwm.c # Libraries to link against LIBS = -lbbb_pwm -lbbb_adc # Default target: build the executable all: $(TARGET) # Build the executable $(TARGET): $(SRC) $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(SRC) $(LIBS) -o $(TARGET) # Clean up build artifacts clean: rm -f $(TARGET) # Phony targets to avoid conflicts with files of the same name .PHONY: all clean -
Setup the following circuit, which is an amalgamation of ADC C Library and PWM C Library circuits
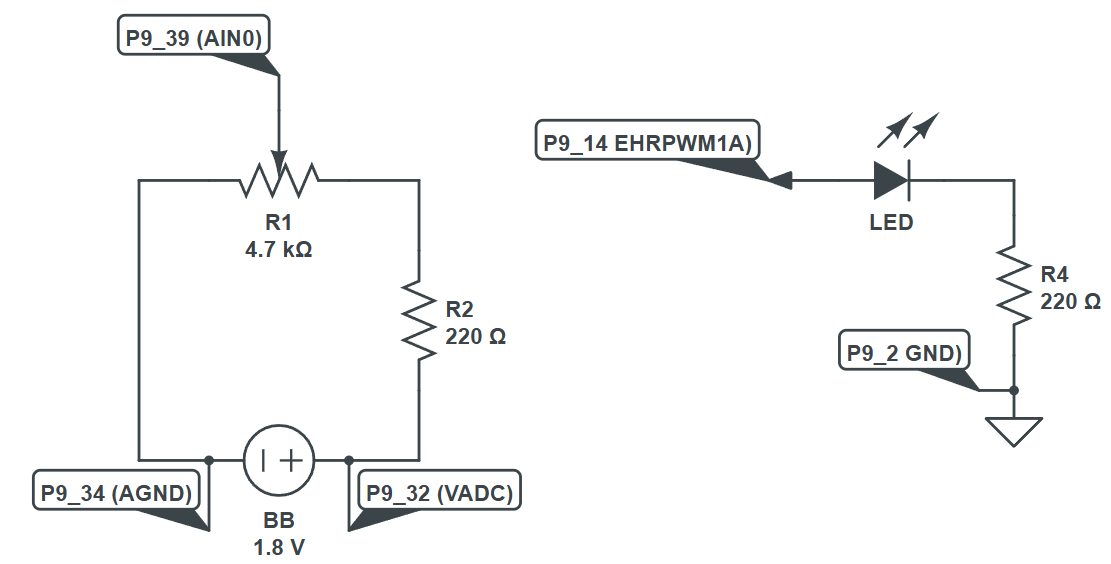
-
When running
./adc2pwmyou may see this terminal output and you have connected up your circuity correctly, the LED should change it's brightness based on the resistance from the potentiometer:Output
Phy: P9_14 Channel: 0 Chip: 0 Period path: /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/period Duty Cycle path: /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/duty_cycle Enable path: /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/enable ADC Reading: 0 ADC Reading: 0 ADC Reading: 283 ADC Reading: 697 ADC Reading: 1313 ADC Reading: 1674 ADC Reading: 1907 ADC Reading: 2454 ADC Reading: 2968 ADC Reading: 3367 ADC Reading: 3687 ADC Reading: 3989 ADC Reading: 3920 ADC Reading: 4001 ADC Reading: 3932 ADC Reading: 3985 ADC Reading: 4002 ADC Reading: 4002 ADC Reading: 4001 ... -
Once you have done that, experiment with the code, can you get a faster response, or a longer run time of the program?