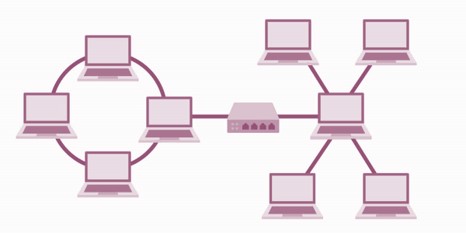
Hybrid topology
Composed of two or more different topologies and are most-commonly encountered in larger enterprises. A mixed bag of capabilities and vulnerabilities.
Advantages
- Flexible, incorporate multiple typologies, very scalable
Disadvantages
- Complex, each sub typology is managed independently of the whole, can be costly to set up, tough job to manage