Learning Python
We will be doing this lab inconjuction with the Python lecture. Key concepts will be explained and you will put into practice.
0. Interpreter for Python
-
We should not need to do anything for the university machines to run python as this is already part of the PATH, you can run the following commands:
So let's make our first program.
Exercises 1. Hello World
-
Frist we need to create a directory and file, call directory
learning_pythonand create a file in side it calledhelloworld.py:
-
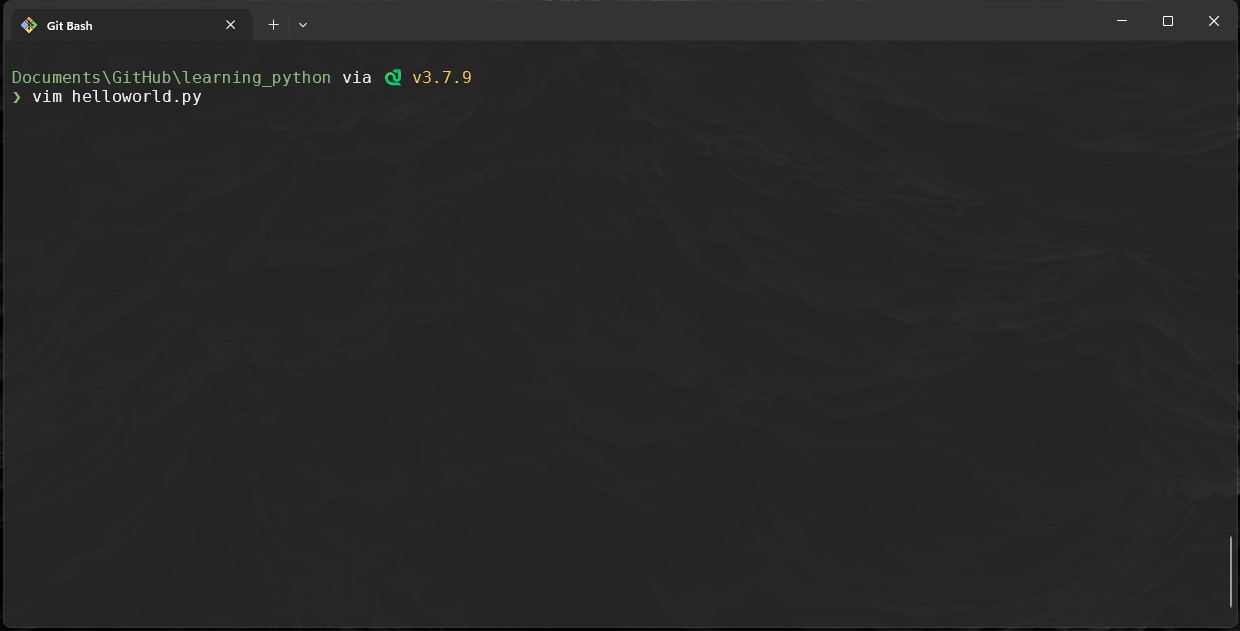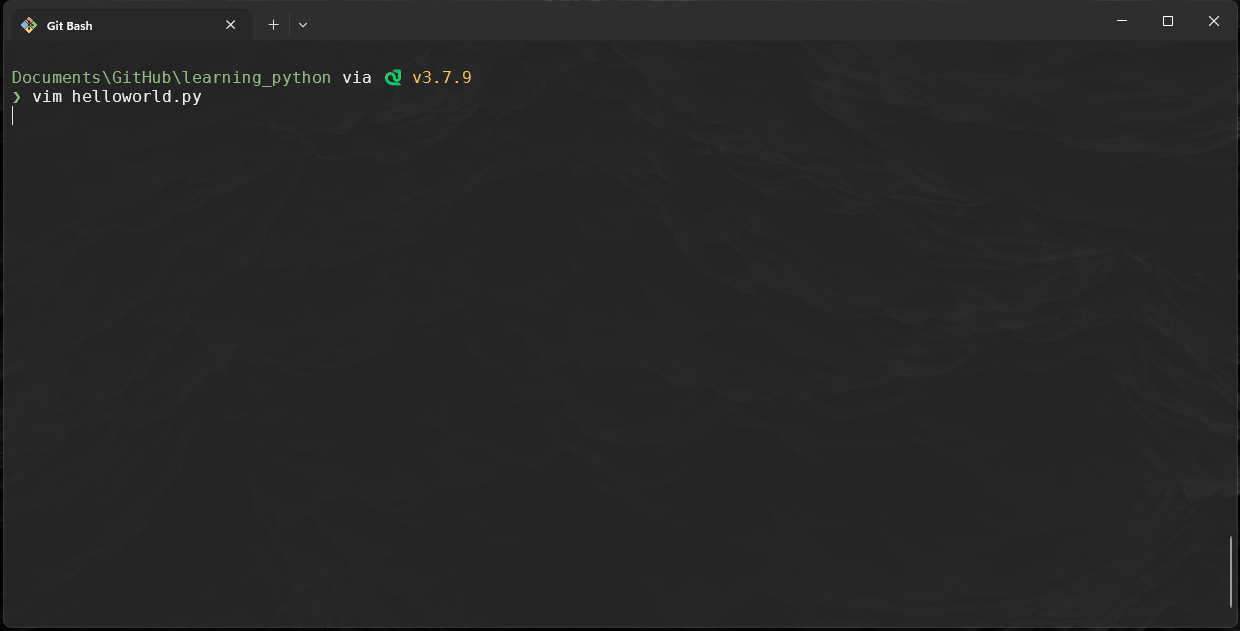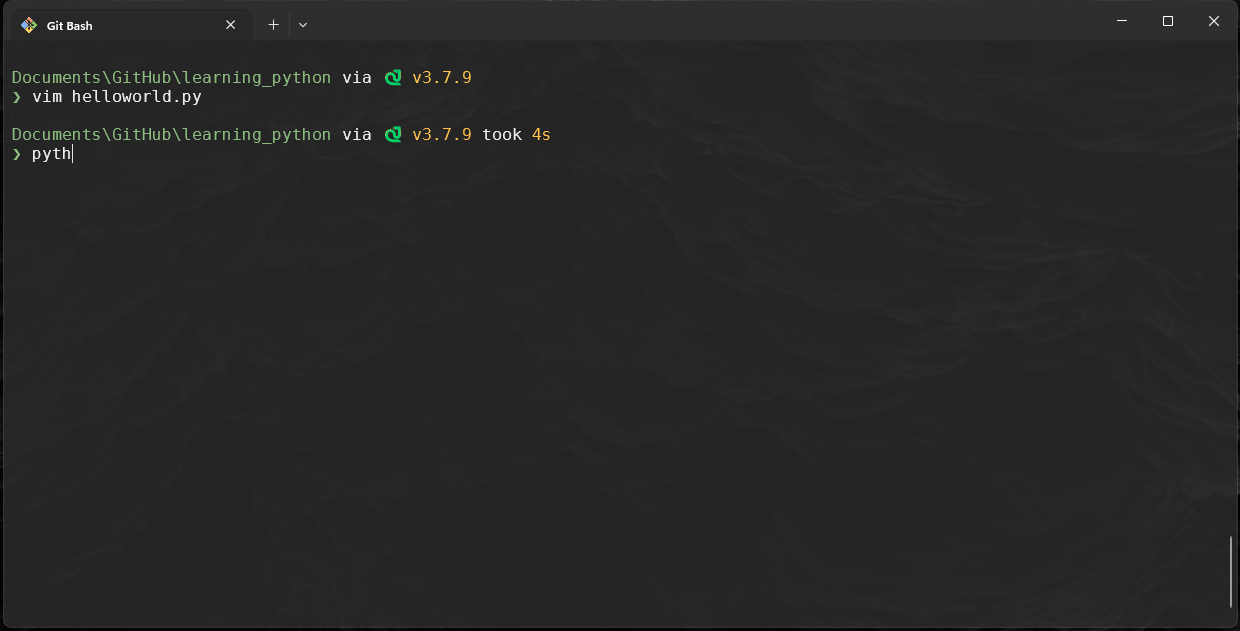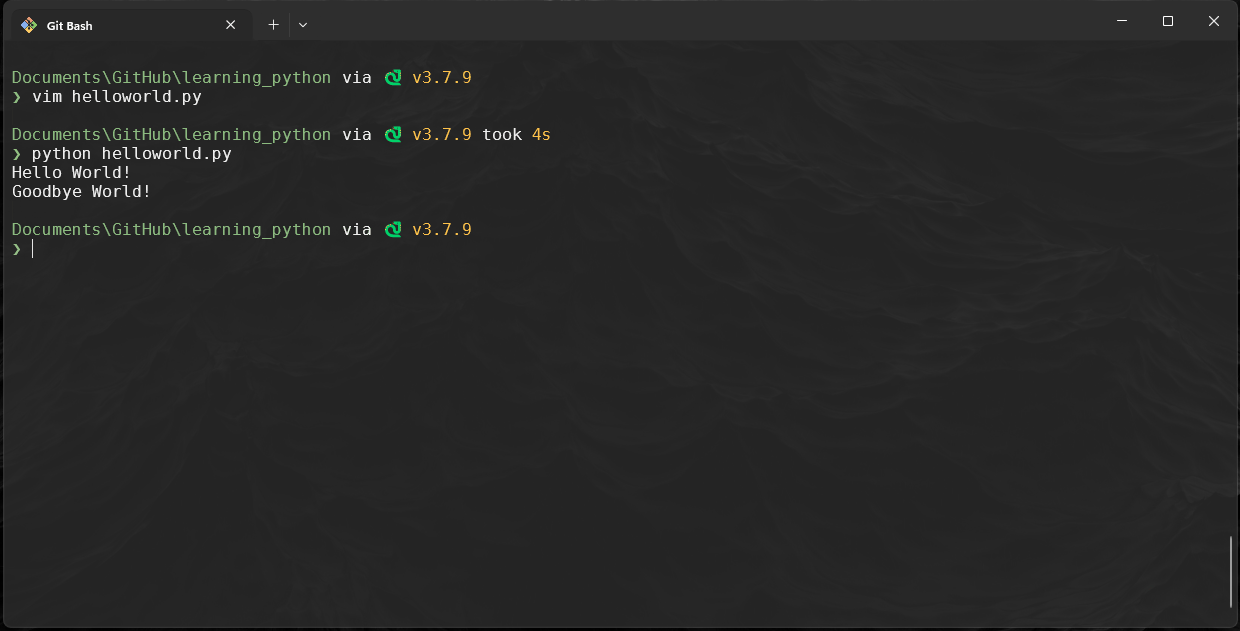
Modify the files content to contain the following:
Exercise 2: Variables and Data Types
Instructions:
-
Create a new file called
variables.py -
Create a variable called
nameand assign it your name as a string. -
Create a variable called
ageand assign it your age as an integer. -
Create a variable called
heightand assign it your height in meters as a float. -
Print each variable on a new line.
-
and then run it.
Exercise 3: Basic Operations
Instructions:
-
Create a new file call it
basicMaths.py -
Create two variables,
aandb, and assign them any two numbers. -
Perform and print the results of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division between
aandb. -
Use the modulus operator to find the remainder of
adivided byband print the result. -
and then run it.
Exercise 4: Lists and Indexing
Instructions:
-
Create a new file called
lists.py -
Create a list called
fruitsthat contains the following fruits:"apple","banana","cherry". -
Print the first fruit in the list.
-
Add a new fruit
"orange"to the list and print the updated list. -
Remove
"banana"from the list and print the list again. -
and then run it
Exercise 5: Conditional Statements
Instructions:
-
Create a file called
conditionals.py -
Write a program that checks if a number is positive, negative, or zero.
-
Assign a value to the variable
numberand useif,elif, andelseto print:"Positive"if the number is greater than 0"Negative"if the number is less than 0"Zero"if the number is exactly 0.
-
and then run it.
-
change
5to0and run again
Exercise 6: Loops
Instructions:
-
Create a file called
loops.py -
Write a
forloop that prints numbers from 1 to 5. -
Create a list of your favorite colors and use a
forloop to print each color. -
Write a
whileloop that prints numbers from 10 down to 1. -
run the program
Exercise 7: Functions
Instructions:
-
Create a new file called
functions.py -
Write a function called
greetthat takes a name as a parameter and prints"Hello, <name>!". -
Write a function
squarethat takes a number as a parameter and returns its square. -
Test both functions by calling them with sample inputs.
def greet(name): print(f"Hello, {name}!") def square(number): return number ** 2 # Testing the functions greet("Alice") print("Square of 4:", square(4))
Exercise 8: Dictionaries
Instructions:
-
Create the a file called
dictionaries.py -
Create a dictionary called
studentwith keys:name,age, andcourses. Assign appropriate values to each. -
Print the student's name and age.
-
Add a new key
graduation_yearwith a sample year and print the updated dictionary. -
and run it.
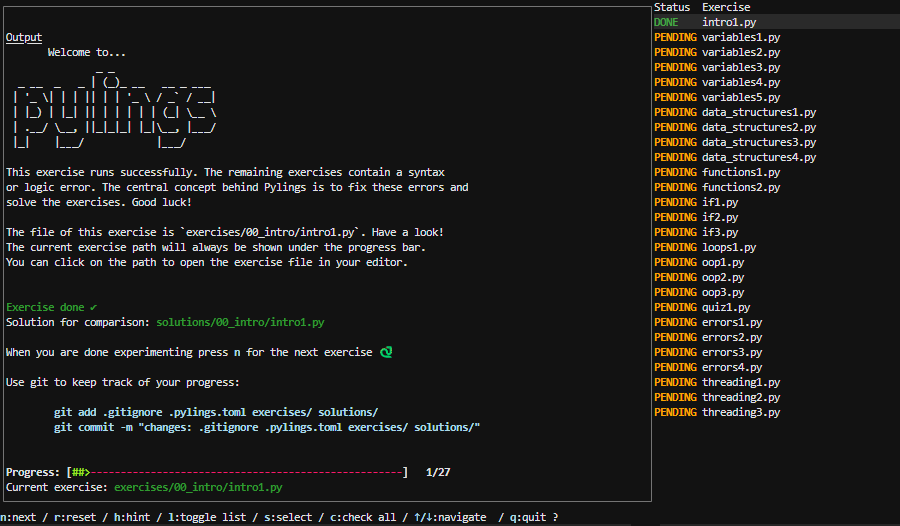
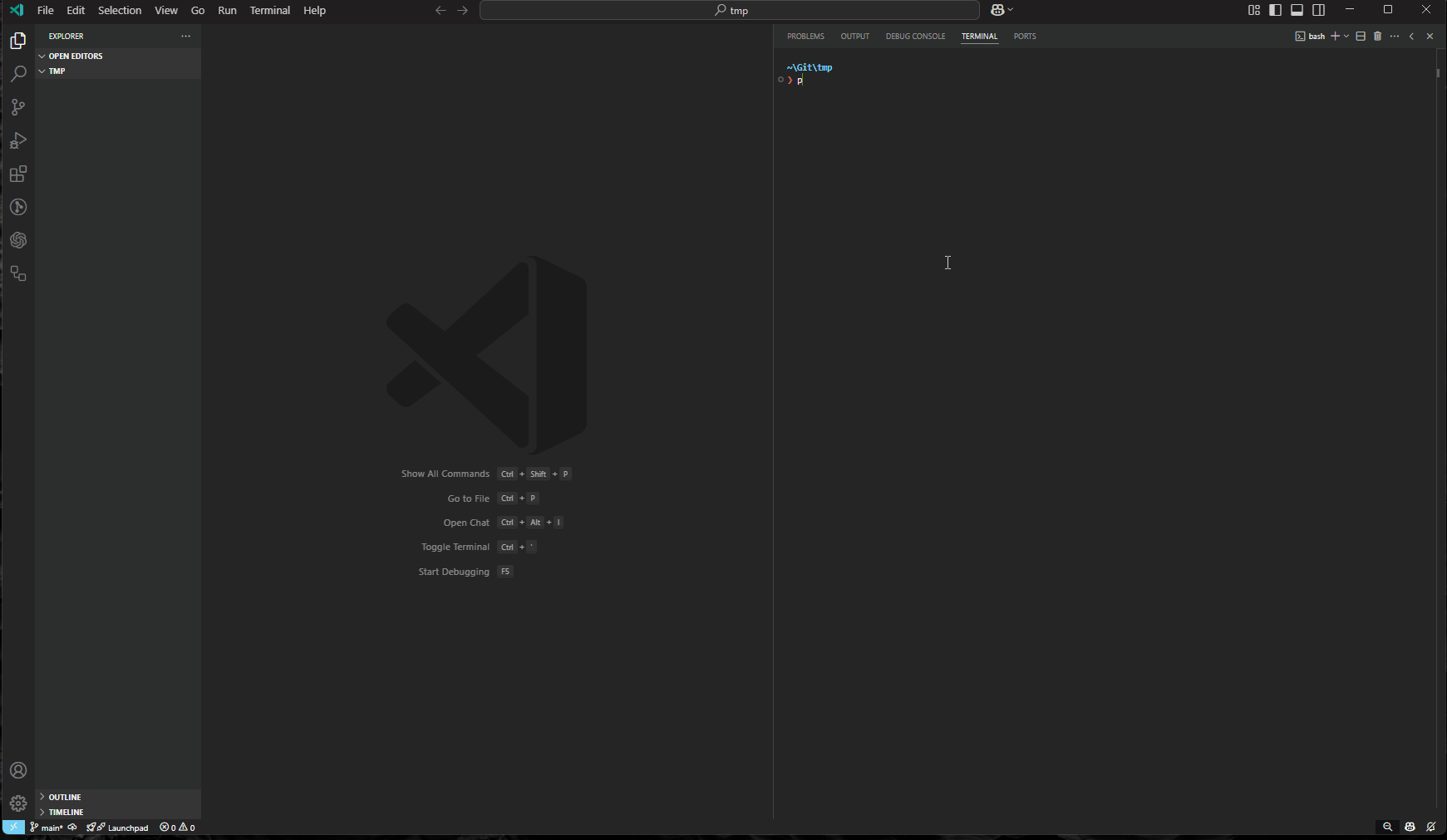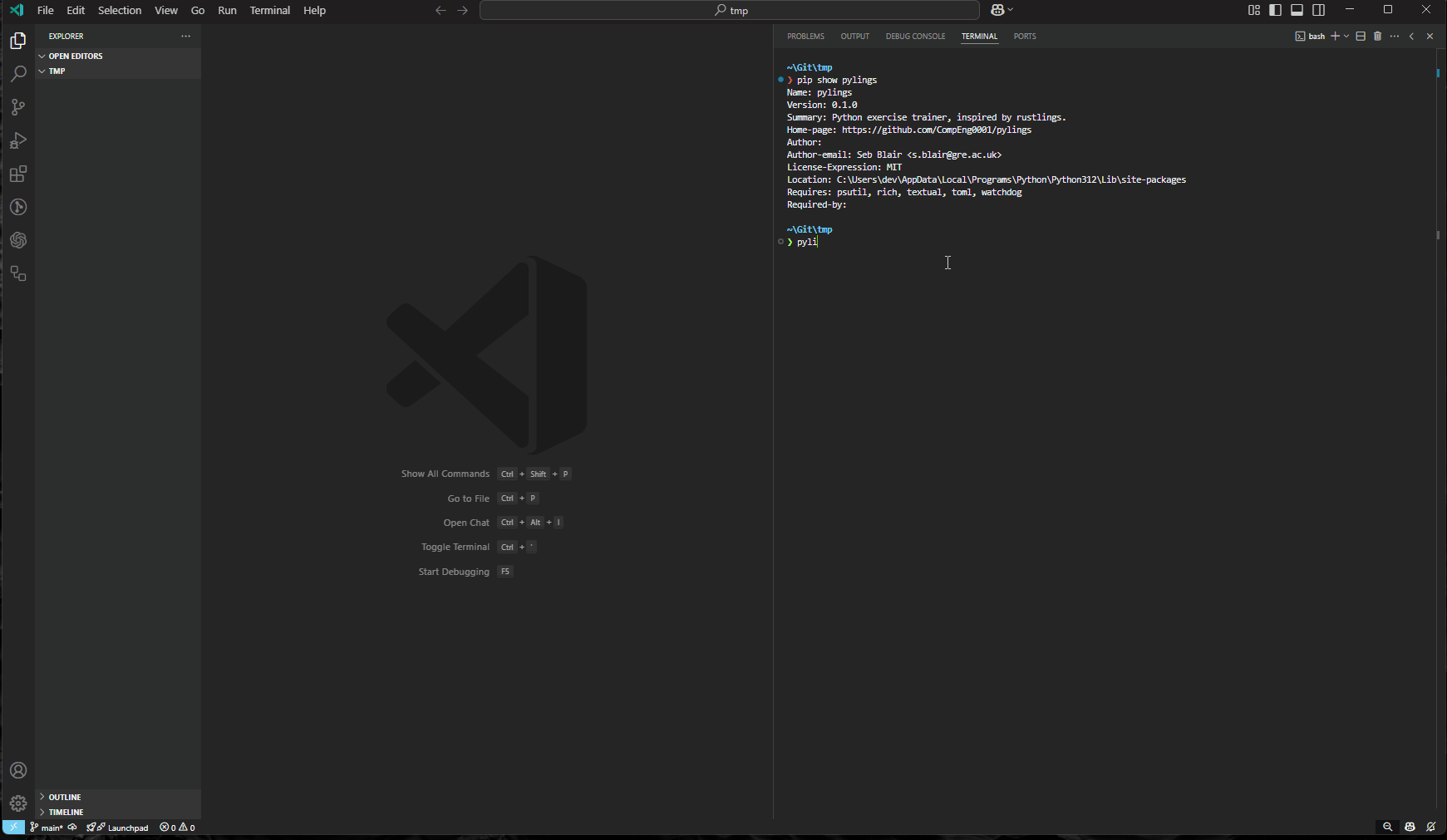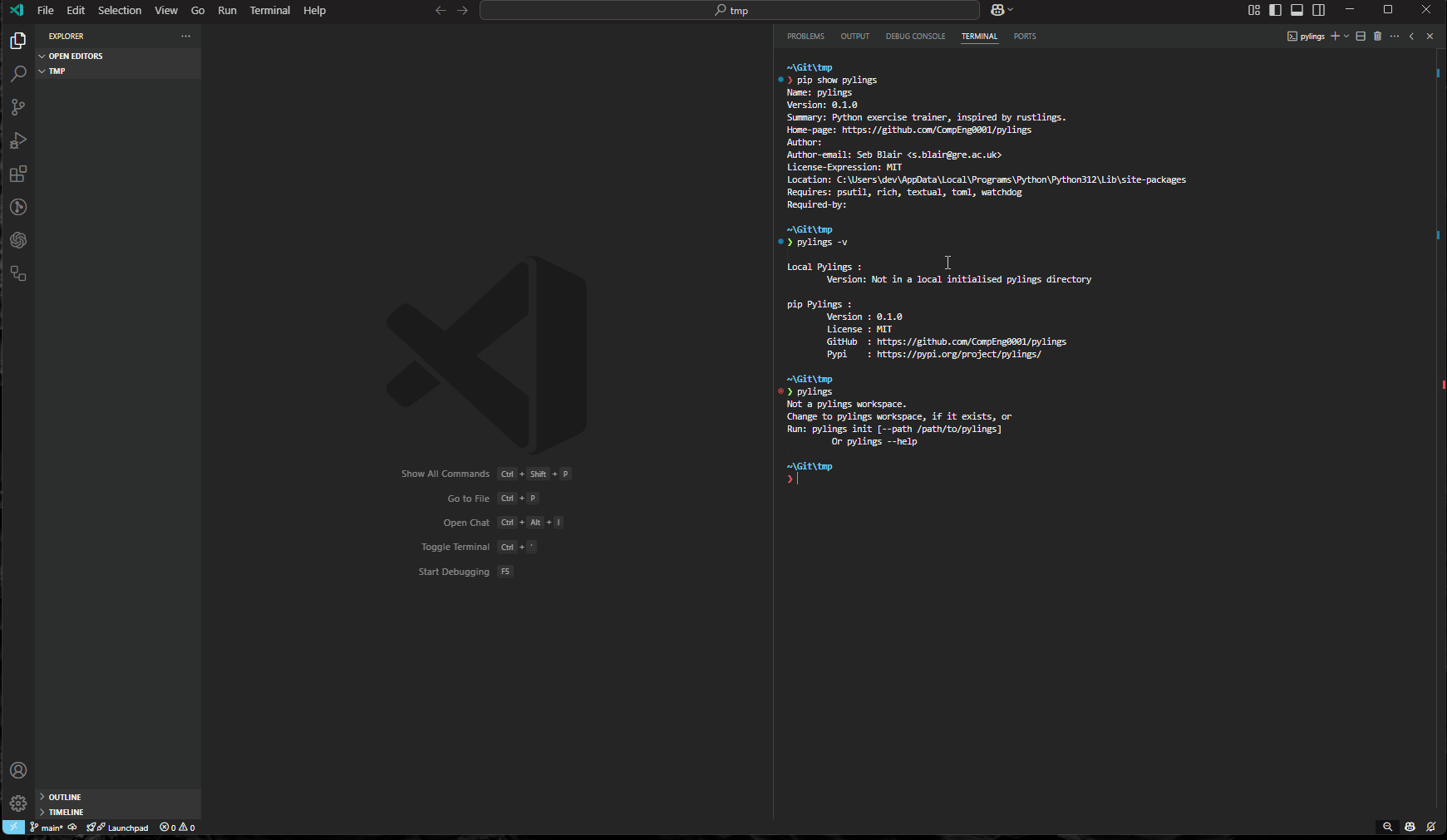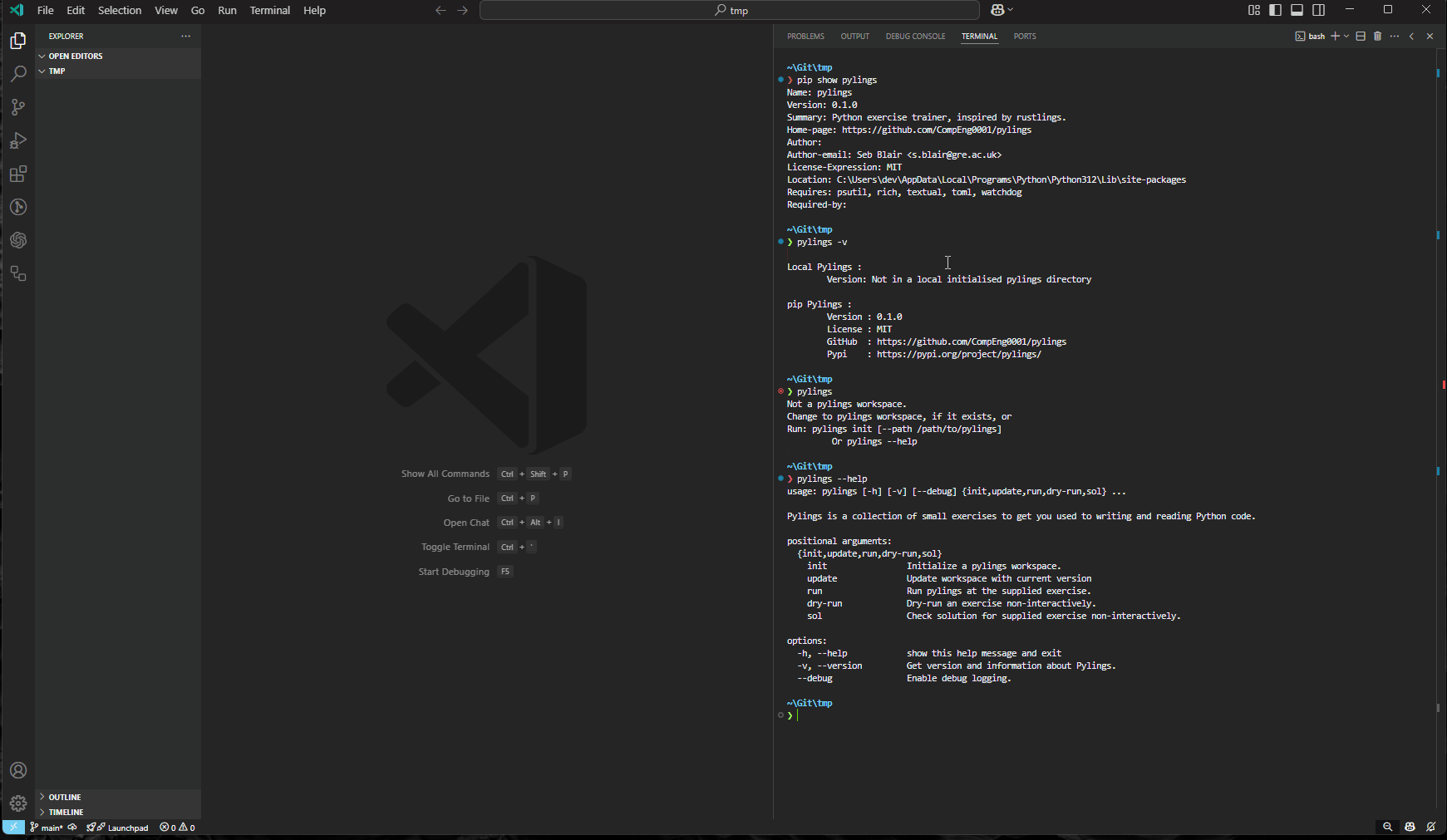
Pylings
Pylings, made by yours truly, is an interactive Python learning tool heavily inspired by the renowned Rustlings. It provides small, focused exercises to help you learn Python by fixing code snippets and experimenting with them.
Pylings is designed to help beginners and experienced developers alike improve their Python skills through hands-on practice. Each exercise covers core Python concepts such as variables, data structures, loops, and more. This includes reading and responding to compiler and interpreter messages!
-
Got to https://github.com/CompEng0001/Pylings and give it a star
- Fork the repo if you want too!
-
If you haven't already download pylings from
pippy -m pip install pylings
For best experience run in Visual Studio Code
Running Pylings
-
Once installed via pip or git, navigate to a directory of your choice...
-
... and run:
py -m pylings init
-
or provide the path as an argument:
py -m pylings init --path path/to/initialise-pylings
-
If a directory already exists with the same name you can use:
py -m pylings init --force [--path path/to/initialise-pylings]
-
-
Then you can launch pylings in the initialised directory
-
py -m pylings
Of course you could always add the following to your PATH, and you call pylings directly:
-
Windows
$HOME/AppData/Local/Programs/Python/Python313/
-
Linux/Unix
$HOME/.local/bin
Working environment
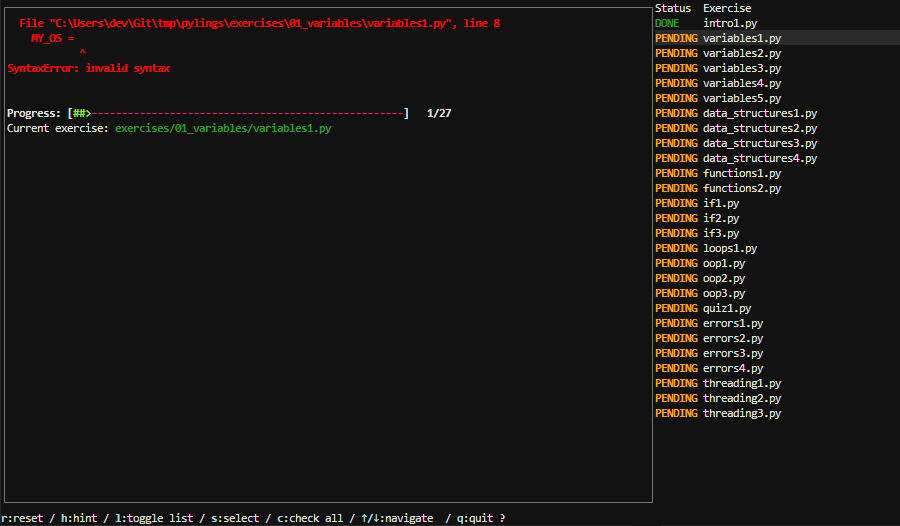
The exercises are sorted by topic and can be found in the subdirectory exercises/
We highly recommend that you have a look at them before you start.
Most exercises contain an error that keeps them from compiling, and it's up to you to fix it!