let module = Module { code: "COMP1856".to_string(), name: "Software Engineering".to_string(), credits: 15, module_leader: "Seb Blair BEng(H) PGCAP MIET MIHEEM FHEA".to_string(), }
Improve development process; product quality and reduce the cost of QA
Support the role of the installer who is not the user or developer, also has no IDE to use. Think organisation IT Support.
push
pull_request
schedule
on: push: branches: - main jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout code uses: actions/checkout@v3 - name: Set up Node.js uses: actions/setup-node@v3 with: node-version: '16' - name: Install dependencies run: npm install - name: Run tests run: npm test
.github/workflows
name: deploy-content concurrency: deploy-content on: push: branches: [ main ] jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: checkout repo uses: actions/checkout@v4 - name: make build directory run: mkdir build/ && cp -r figures build/figures - name: build index uses: docker://marpteam/marp-cli:latest with: args: index.md -o build/index.html env: MARP_USER: root:root - name: build content html uses: docker://marpteam/marp-cli:latest with: args: -I content/ -o build/content/ --html --allow-local-files --theme themes/uog-theme.css env: MARP_USER: root:root - name: deploy content if: ${{ github.event_name == 'push' }} uses: JamesIves/github-pages-deploy-action@v4 with: branch: gh-pages folder: ./build/
name: Deploy Website on: push: branches: - main jobs: deploy: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout code uses: actions/checkout@v3 - name: Build website run: | npm install npm run build - name: Deploy to GitHub Pages uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3 with: github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} publish_dir: ./dist
Workflow Logs:
Enable Debugging:
ACTIONS_STEP_DEBUG
Common Issues:
<div class="columns-2" > <div style="padding-top:250px"> - Modern CI and CD practices are referred to as a CI/CD pipeline and can handle every stage of the build process from commit to deployment. </div> <div style="padding-top:225px"> 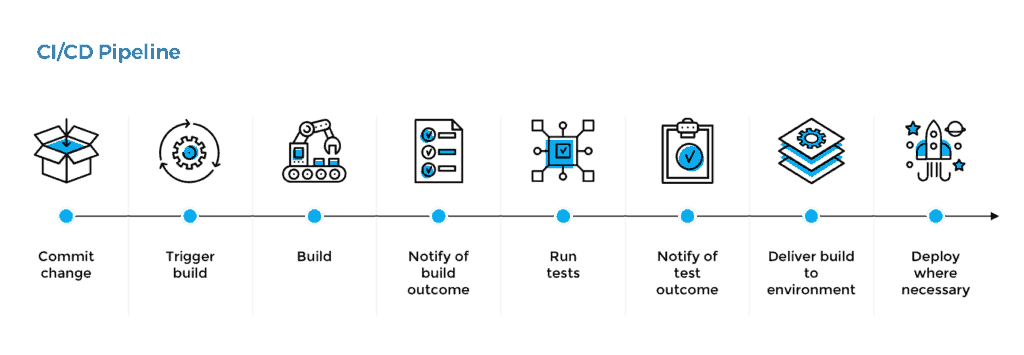 </div> </div>